sm 기술 블로그
150. 13305(주유소) - 자바 본문
import java.util.*;
import java.io.*;
import java.math.BigInteger;
class Main {
public static void main(String[] args) throws IOException {
BufferedReader br = new BufferedReader(new InputStreamReader(System.in));
int N = Integer.parseInt(br.readLine());
BigInteger result = new BigInteger("0");
int start = 0;
long[] road = new long[N - 1];
long[] city = new long[N];
String[] roadTmp = br.readLine().split(" ");
for (int i = 0; i < roadTmp.length; i++) {
road[i] = Long.parseLong(roadTmp[i]);
}
String[] cityTmp = br.readLine().split(" ");
for (int i = 0; i < city.length; i++) {
city[i] = Long.parseLong(cityTmp[i]);
}
for (int i = 1; i < city.length; i++) {
if (i == city.length - 1) {
for (int j = start; j < road.length; j++) {
result = result.add(BigInteger.valueOf(road[j] * city[start]));
// result += (long) (road[j] * city[start]);
}
}
else if(city[start] > city[i]) {
for (int j = start; j < i; j++) {
result = result.add(BigInteger.valueOf(road[j] * city[start]));
// result += (long) (road[j] * city[start]);
}
start = i;
}
else continue;
}
System.out.println(result);
}
}문제요약
왼쪽 도시부터 오른쪽 도시까지 최소의 주유비용으로 가시오
설명

다음과 같이 원안에는 가스비용 선 위에는 도로 길이라고 하자.
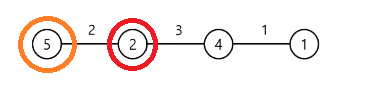
현재 두번째 도시가 첫번째 도시보다 주유 비용이 싸다.
때문에 일단 두번째 도시로 이동하기 위해서 5*2의 비용을 지불하고 두번째 도시로 넘어가야 한다.

하지만 세번째 도시는 두번째 도시보다 가격이 비싸다.
때문에 두번째 도시에서 네번째 도시까지 갈 수 있게 주유한다면 최소의 비용으로 도착이 가능하다.
따라서
만약 비교 도중에 주유비가 더 적은 도시를 만난다면, 주유비가 최소라고 생각했던 부분을 기점으로 더 적은 부분이 도달 할 수 있을 정도 까지 주유를 하고 더 적은 쪽에서 부터 다시 주행을 시작하면 된다.
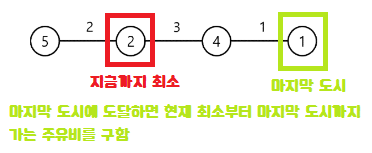
다시 예를 들면

import java.util.*;
import java.io.*;
import java.math.BigInteger;
class Main {
public static void main(String[] args) throws IOException {
BufferedReader br = new BufferedReader(new InputStreamReader(System.in));
int N = Integer.parseInt(br.readLine());
BigInteger result = new BigInteger("0");
int start = 0;
long[] road = new long[N - 1];
long[] city = new long[N];
String[] roadTmp = br.readLine().split(" ");
for (int i = 0; i < roadTmp.length; i++) {
road[i] = Long.parseLong(roadTmp[i]);
}
String[] cityTmp = br.readLine().split(" ");
for (int i = 0; i < city.length; i++) {
city[i] = Long.parseLong(cityTmp[i]);
}전반부 입력을 받는 부분이다.
값이 매우 커질 수 있기 때문에 result는 BigInteger를 사용하였다.
각 도로, 도시 또한 int를 넘을 수 있는 크기의 값이 들어 올 수 있기 때문에 long 배열 형태로 선언하였다.
for (int i = 1; i < city.length; i++) {
if (i == city.length - 1) {
for (int j = start; j < road.length; j++) {
result = result.add(BigInteger.valueOf(road[j] * city[start]));
// result += (long) (road[j] * city[start]);
}
}
else if(city[start] > city[i]) {
for (int j = start; j < i; j++) {
result = result.add(BigInteger.valueOf(road[j] * city[start]));
// result += (long) (road[j] * city[start]);
}
start = i;
}
else continue;
}최소 주유비를 구하는 로직이다.
먼저 else if 부분 부터 설명 하겠다.
else if(city[start] > city[i]) {
for (int j = start; j < i; j++) {
result = result.add(BigInteger.valueOf(road[j] * city[start]));
// result += (long) (road[j] * city[start]);
}
start = i;
}지금까지 최소 비용(start) > 현재 비용 이라면 즉, 현재 비용이 더 낮다면,
start 인덱스 부터 현재 비용인덱스 전까지 도시 * 로드를 진행한다.
예를들어
입력이
7
3 4 2 2 4 5
8 9 5 4 2 7 1다음과 같다면
지금까지 최소비용(start)는 8이고, 현재 최소 비용은 5이다.
따라서 8*3 + 8*4 를 진행한다.
그리고 지금까지 최소 비용을 현재 최소 비용의 인덱스로 저장한다.
BigInteger 사용법은 아래를 참고하자.
https://smhope.tistory.com/297
[Java] BigInteger
BigInteger란? int나 double은 크기 제한이 있기 때문에 매우매우 큰 수는 표현이 불가능하다. 그에 반해 BigInteger는 문자열 형태로 이루어져있기 때문에 숫자 범위를 무한하게 표현이 가능하다. 선언 /
smhope.tistory.com
if (i == city.length - 1) {
for (int j = start; j < road.length; j++) {
result = result.add(BigInteger.valueOf(road[j] * city[start]));
// result += (long) (road[j] * city[start]);
}
}마지막 도시에 도달한 경우이다.(배열은 0부터 시작이기 때문에 길이 - 1이 마지막 도시이다.)
그러면 더이상 나아갈 곳이 없으니 지금까지 최소비용(start)을 가지고 진행되지 않은 도로의 값들을 계산해준다.
else continue;continue를 통해서 현재 가지고 있는 비용이 최소이면 다음으로 넘어간다.
'문제 > 백준_자바' 카테고리의 다른 글
| 153. 9012(괄호) - 자바 (0) | 2022.07.21 |
|---|---|
| 151. 10828(스택) - 자바 (0) | 2022.07.20 |
| 149. 1541(잃어버린 괄호) - 자바 (0) | 2022.07.18 |
| 148. 11399(ATM) - 자바 (0) | 2022.07.18 |
| 147. 1931(회의실 배정) - 자바 (0) | 2022.07.17 |


